Risks Involved with an Inaccurate Pupil Diameter Measurement
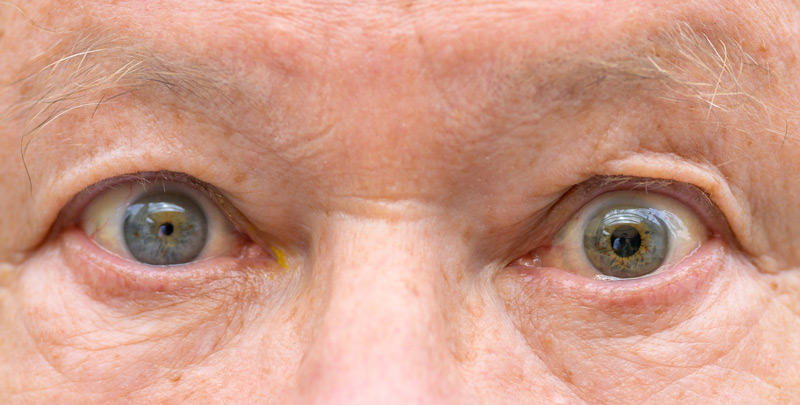
Accuracy is essential in any measurement, especially when a doctor is measuring the pupil diameter of their patients. A patient’s eye and brain health depend on it, so health professionals must get an accurate reading during every pupil exam. If there are any errors with their measurements, this can lead to issues such as misdiagnosis, improper treatment, or even injury.
But doctors can take steps to ensure they get an accurate reading each time. They should be familiar with the different factors that can cause inaccurate measurements and how to reduce their impact on results.
This article will explore some of the most common factors that can lead to inaccurate measurements and how to avoid them.
1. Difficult to determine the condition of the optic nerve
The optic nerve is a nerve that connects the eye to the brain. It can be challenging for doctors to determine if the optic nerve is healthy, leading to inaccurate readings. When doctors are measuring the pressure inside the eye, they need to know whether there are any abnormalities in the optic nerve.
If there is damage to this nerve, it can cause bleeding into the retina and affect vision—which is why doctors must measure intraocular pressure accurately.
2. A possible underestimation of aphakia
Doctors often rely on intraocular pressure measurement to determine whether someone has aphakia. But this may not be accurate in all cases. If there is damage to the cornea, it can lead to inaccurate readings.
Therefore, doctors need to consider the cornea’s condition when measuring intraocular pressure. If it’s scratched or damaged, they should come up with another way of diagnosing an aphakia.
3. Misdiagnosis of traumatic brain injuries
Traumatic brain injuries are usually hard to diagnose, especially when they are not immediately apparent. This is partly because doctors may attribute symptoms like dizziness and loss of consciousness to other causes.
For example, some people with traumatic brain injuries experience nausea and vomiting after the accident, which can easily be mistaken for a hangover or food poisoning.
This can be risky because it delays the diagnosis and treatment of a brain injury, making it more difficult to recover.
4. Significant patient discomfort or pain
One duty of a doctor is to reduce the patient’s pain. However, it can sometimes be difficult for a doctor to determine whether the pain is due to an injury or another health problem. This is especially true for patients with traumatic brain injuries because they may not have outward signs of pain, such as blood or swelling.
Since pupillary size measurement is a good way of knowing the state of the brain, the doctor will be less likely to diagnose a traumatic brain injury when there’s an inaccurate pupil measurement.
5. Medication wastage, with consequent treatment costs increases
Inaccurate pupil measurements can lead to unnecessary medical treatment. For instance, if a doctor incorrectly diagnoses someone as having an eye problem when they have a traumatic brain injury, they will probably prescribe the wrong medication for the patient’s condition.
This means that doctors waste a significant amount of medication, and patients are treated for conditions requiring different treatments. This can lead to increased medication costs and result in unnecessary patient suffering.
What is the best tool for pupil measurement?
Health professionals can use various tools to measure the pupil, but many are inaccurate enough to be used precisely.
For example, the swinging flashlight test is not a reliable method for measuring the pupil because it is a subjective test. This means that each time the doctor measures the patient’s pupils using this method; they must rely on their judgment when determining whether their pupils are dilated.
However, the best method of pupil measurement is to use a pupilometer. Pupilometers are handheld devices that have been of immense help in ensuring that pupils are measured accurately. They have been designed to give the doctor an objective pupil size measurement, and doctors can use them for adults and children.
These instruments are non-invasive and portable devices, and health experts can use them in most clinical settings. They have the advantage of being able to measure the size of both pupils at once, which is not possible with manual methods.




